Delph INS Subsea Overview
Delph INS Subsea is a software allowing visualizing, post-processing and exporting data recorded by the INS.
In order to enhance the post-processing performance, it also allows including private or public GNSS base station and downloading GNSS base station from public servers using the GNSS Download Tool (GDT), which is launched directly from the Delph INS Subsea.
Post-processing overview
The overall work flow of Delph INS Subsea is described in the following figure.
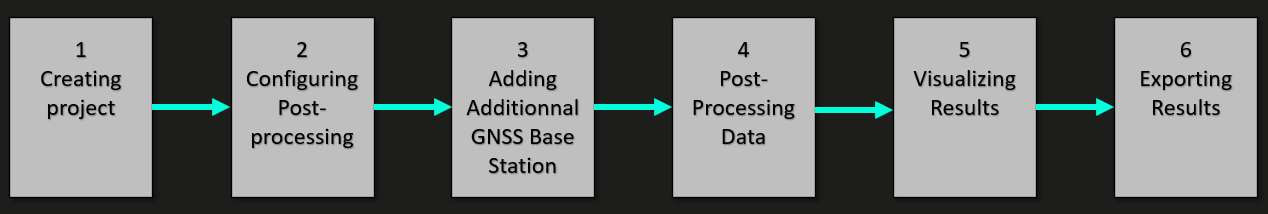
Delph INS Subsea overview
Consequently, the post-processing of the data is usually divided in the following steps:
| 1. | Formatting data for Delph INS Subsea |
Delph INS Subsea processes data in the XPF (Exail proprietary) or the UBX (Ublox proprietary) formats. The INS raw data recorded is not in the *.xpf format, it consequently must be converted to the XPF format. This can be done by creating a project with the Delph INS Subsea.
| 2. | Configuring post-processing |
The INS configuration during the survey is saved in the post-processing file, but you may want to modify some settings. For instance if the GNSS lever arms were not correctly input, this can be changed afterward. Besides, you can set up the output (output data rate, lever arms, etc.). It is also possible to add calibration in order to have better estimation of lever arms. This is done in the Processing panel of the Delph INS Subsea.
| 3. | Adding additional GNSS base stations |
Additional data, especially GNSS base station, can be added. The GNSS base station can either be recorded by the user, or downloaded from a public base station server available on Internet. The selection of relevant public base station can easily be done using the GNSS Download Tool (GDT), which can be launched directly from the Delph INS Subsea.
| 4. | Post-processing data |
Once the set-up is completed, data can be post-processed with the Start button of the Delph INS Subsea.
| 5. | Visualizing results |
After the post-processing, it is often useful to do a visual inspection of the results to verify that the processing was correct. It is for instance recommended to check that the GNSS is consistently used by the INS.
| 6. | Exporting results |
The results can then be exported to various predefined formats or to an user-defined format in order to meet any user requirement.